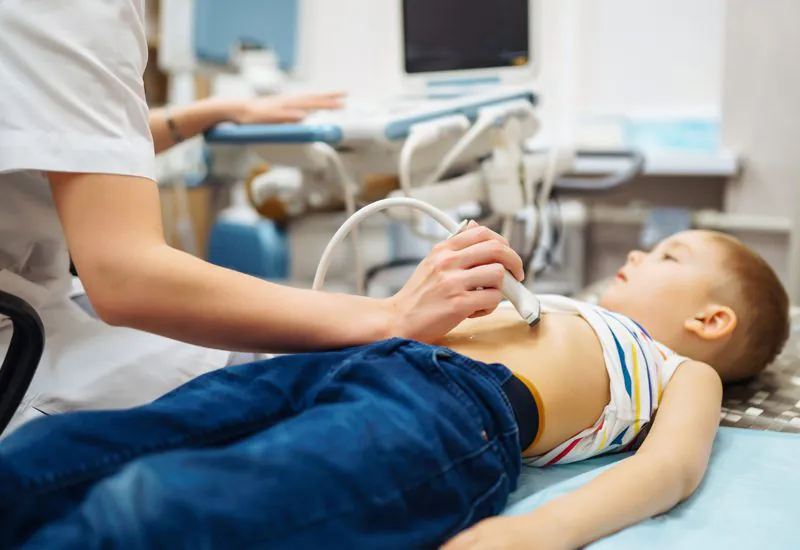
Doppler ultrasound uses sound waves to assess blood flow, aiding diagnosis with safe, precise imaging.
Doppler ultrasound uses sound waves to assess blood flow, aiding diagnosis with safe, precise imaging.
Doppler ultrasound is a special ultrasound imaging technique that evaluates blood flow through a blood vessel, including the body’s major arteries and veins in the abdomen, arms and legs. Doppler ultrasound is also used to identify blood flow blockages in the neck arteries that could lead to a stroke. A Doppler ultrasound can measure the direction and speed of blood flow and allows for real-time viewing of blood flow that can’t be obtained with other methods. It can help your doctor identify narrowing or blockages (such as clots or plaque), defects or tumors and determine the most effective treatment. Doppler ultrasound is also useful in monitoring sites prior to bypass surgery, angioplasty or stenting.
Color Doppler & Power Doppler
Color Doppler
Converts the blood flow measurements into an array of colors to help show the speed and direction of blood flow through the vessel.
Power Doppler
More sensitive than Color Doppler in detecting blood flow, although it does not provide information about the direction of blood flow. Power Doppler provides even greater detail about blood flow, especially in blood vessels located inside organs.
High image quality and speed
Advanced Radiology uses the Aixplorer® MultiWave™ ultrasound system with the latest technology for enhanced image quality and ultra-sensitive blood flow measurement. This system also features UltraFast™ Doppler which makes exams quicker and more accurate. The system uses ultra-high imaging rates that are up to ten times faster than conventional Color Doppler
Preparation
Ultrasound exams are pain-free and usually take 30 minutes. Some tests can take up to 90 minutes. The technologist places gel on the skin of the area to be examined, and then moves the ultrasound transducer, or wand, over the skin.
No preparation is required.
What To Expect
Color Doppler
Uses standard ultrasound methods to produce a picture of a blood vessel. Also, a computer converts the Doppler sounds into colors that are overlaid on the image of the blood vessel and that represent the speed and direction of blood flow through the vessel.
Power Doppler
A special type of color Doppler. Power Doppler can get some images that are hard or impossible to get using standard color Doppler. Power Doppler is most commonly used to evaluate blood flow through vessels within solid organs.
Elastography
Ultrasound Elastography allows our radiologists to map the elastic properties of soft tissue. High-frequency sound waves are used to measure the softness or hardness of tissue, which helps your doctor diagnose or track certain conditions and diseases. Elastography may be used on numerous organs and tissues, including the liver and breast. It can help differentiate between malignant (cancerous) and benign (non-cancerous) tissues, identify changes in muscles and tendons, as well as assess liver fibrosis.
Fast, non-invasive liver assessments
Using ShearWave™ Elastography with UltraFast™ Imaging, Advanced Radiology helps patients manage chronic liver disease. ShearWave Elastography is a real-time, non-invasive way to stage liver fibrosis. These exams can take as little as 60 seconds (up to 5 minutes). UltraFast™ Imaging acquires 20,000 images per second—200 times faster than conventional ultrasound. Using this advanced technology may reduce the number of liver biopsies since elastography can validate the absence of fibrosis.
Preparation
Ultrasound exams are pain-free and usually take 20 to 30 minutes. The technologist places gel on the skin of the area to be examined, and then moves the ultrasound transducer, or wand, over the skin.
Morning Appointments
Nothing to eat or drink (except clear liquids) from midnight (12:00 AM) the evening before the exam. No breakfast or water in the morning. If you take oral medications, please take them with a minimal amount of water or, bring the medication to the office and take it immediately following the study.
Afternoon Appointments
5-hour food and liquid fast. Any meal before the fast cannot have dairy or fat within it.
General Abdominal Ultrasound
An abdominal ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to produce pictures of the organs and other structures in the upper abdomen. The exam can include the kidneys, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen and the blood vessels like the abdominal aorta. It is a non-invasive way to diagnose abdominal pain, abnormal liver function, kidney or gallbladder stones or an aortic aneurysm (a weakness in the wall of artery from the heart).
Fast, non-invasive assessments – done by request of the referring physician
Advanced Radiology uses the Aixplorer® ultrasound system with ShearWave™ elastography, which takes non-invasive tissue elasticity measurements of abdominal organs like the liver. By measuring the softness or hardness of tissues, your doctor can provide a more accurate diagnosis.
ShearWave™ elastography allows for faster and more accurate imaging of liver disease. The test takes as little as 60 seconds (up to 5 minutes) and provides staging of liver fibrosis in a non-invasive way. This new technology allows your doctor to accurately track disease progression and may reduce the number of biopsies needed.
Preparation
Ultrasound exams are pain-free and usually take 20 to 30 minutes. The technologist places gel on the skin of the area to be examined, and then moves the ultrasound transducer, or wand, over the skin.
Morning Appointments
You should fast—have nothing to eat or drink (except clear liquids—from midnight (12:00 AM) the evening before the exam. No breakfast or water in the morning. If you take oral medications, please take them with a minimal amount of water or, bring the medication to the office and take it immediately following the study.
Afternoon Appointments
Please eat no food during the 5 hours prior to the exam. Any meal before the fast cannot have dairy or fat in it.
Renal Ultrasound Preparation
A renal or retroperitoneal ultrasound is used to evaluate the kidneys and nearby structures. It is very important for your bladder to be full when you arrive since the distended bladder allows the radiologist to fully visualize the structures of the abdomen.
You must drink one quart of water (four 8-oz. glasses) and FINISH it one hour before the exam.
You MAY NOT URINATE after you’ve finished drinking the water.
You may eat normally for breakfast and/or lunch.
Thyroid and Small Parts Ultrasound
Ultrasound of the thyroid uses high-frequency sound waves to generate pictures of the thyroid gland and the surrounding neck tissue. It’s common for patchy areas or nodules to develop on the thyroid. Ultrasound images allow your doctor to evaluate these lumps or nodules to determine if they are benign (non-cancerous), or if they seem more suspicious and may require an Ultrasound-Guided-Biopsyto be certain.
What To Expect
Thyroid ultrasound exams are pain-free and usually take 30 minutes. The technologist places gel on the skin of your neck area, then moves the ultrasound transducer, or wand, over the skin.
Preparation
No preparation is required.
Women’s Ultrasound Imaging
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to generate images the radiologists can view in real time. The sound waves bounce off interior tissues and organs and the return echoes create images. Ultrasound is a useful, non-invasive way for your doctor to evaluate symptoms like pain, swelling and infection.
Breast Ultrasound
Breast ultrasound is frequently used to evaluate a breast lump or area of concern found during a breast exam or mammogram. The exam helps determine if the area is a cyst, fluid-filled or a solid tumor. Advanced Radiology uses the Aixplorer® ultrasound system with patented ShearWave™ Elastography technology that provides clear, distinct imaging to help identify previously unseen lesions and may reduce the number of unnecessary biopsies. Depending on the results of this exam, an Ultrasound-Guided-Biopsy may still be required. Since ultrasound provides images in real time, it is used to guide biopsy procedures to obtain an accurate tissue sample for analysis.
Pelvic Ultrasound
A pelvic ultrasound helps diagnose problems when a woman experiences pelvic pain, abnormal bleeding or other menstrual problems. It generates images of the structures and organs in the lower abdomen and pelvis, including reproductive organs, including uterus, cervix, fallopian tubes, ovaries and bladder. Ultrasound helps identify uterine fibroids, polyps, malignancies, endometrial adhesions or atrophy. Some pelvic ultrasound exams are conducted by placing the ultrasound transducer (wand or probe) directly on the skin of the abdomen, while some exams require a transducer be placed inside the vagina to provide the most detailed images.
What To Expect
Ultrasound exams are pain-free and usually take 20 to 30 minutes. The technologist places gel on the skin of the area to be examined, and then moves the ultrasound transducer, or wand, over the skin.
Breast Ultrasound Preparation
No preparation is required.
If a biopsy is to be performed, no aspirin should be taken for 5-7 days prior to the procedure.
Pelvic Ultrasound Preparation
It is very important for your bladder to be full when you arrive since the distended bladder allows the radiologist to fully visualize the structures of the abdomen.
You must drink one quart of water (four 8-oz. glasses) and FINISH it one hour before the exam.
You MAY NOT URINATE after you’ve finished drinking the water.
You may eat normally for breakfast and/or lunch.
Transvaginal Ultrasound Preparation
If you HAVE NOT had a transvaginal ultrasound at Advanced Radiology before, it is very important for your bladder to be full when you arrive, since the distended bladder allows the radiologist to fully visualize the structures of the abdomen
- You must drink one quart of water (four 8-oz. glasses) and FINISH it one hour before the exam.
- You MAY NOT URINATE after you’ve finished drinking the water.
- You may eat normally for breakfast and/or lunch.
If you HAVE had a transvaginal ultrasound at Advanced Radiology before, there is no preparation.
- You will be asked to empty your bladder prior to the exam.
Call To Schedule
Fairfield / Interventional Imaging– 1055 Post Rd.
Orange – 297 Boston Post Rd.
Stamford – 1259 E Main St.
Stratford – 2876 Main St.
Trumbull / Advanced Women’s Imaging – 15 Corporate Dr.
Wilton – 60 Danbury Rd.
Fairfield / Interventional Imaging– 1055 Post Rd.
Orange – 297 Boston Post Rd.
Stamford – 1259 E Main St.
Stratford – 2876 Main St.
Trumbull / Advanced Women’s Imaging – 15 Corporate Dr.
Wilton – 60 Danbury Rd.



